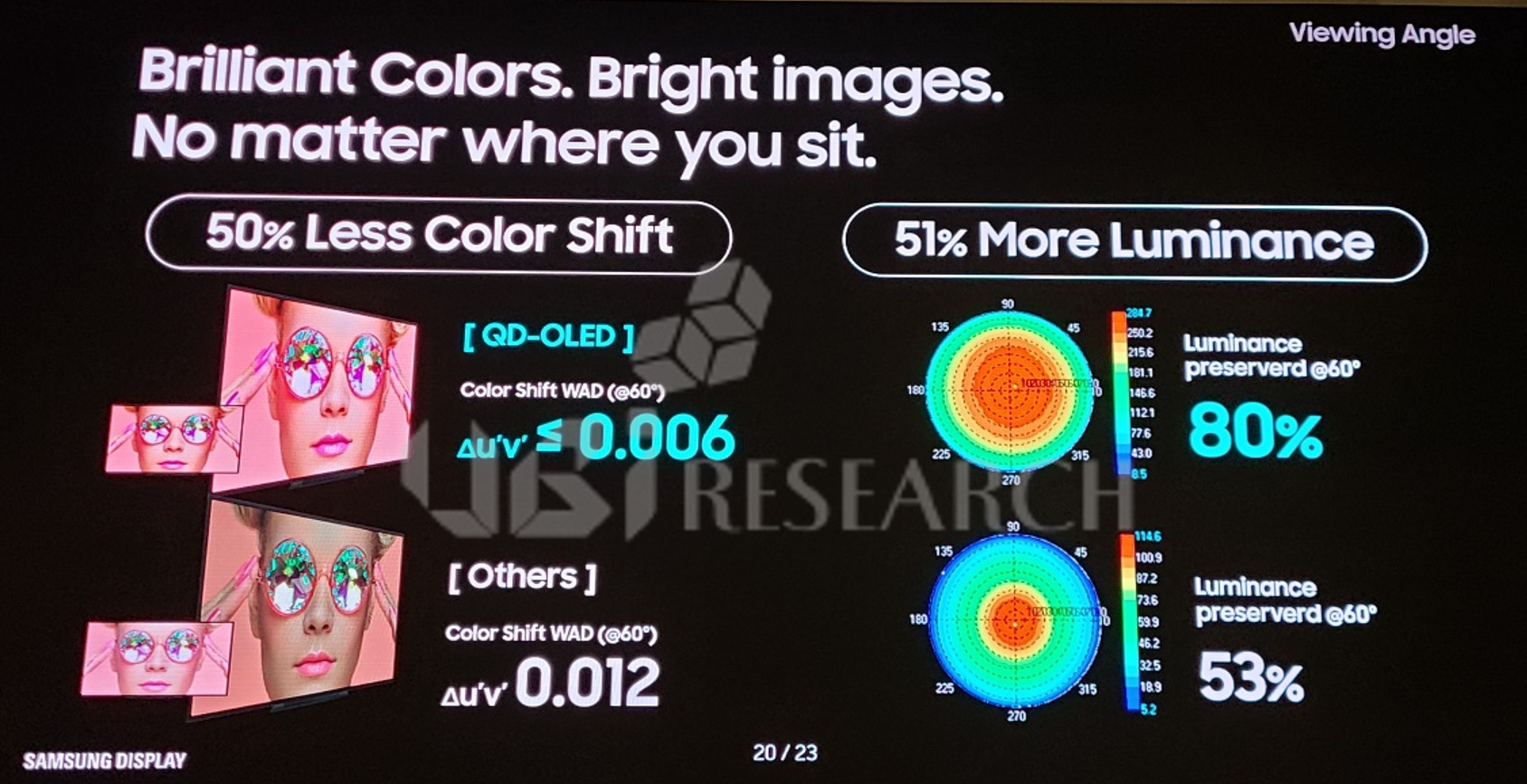
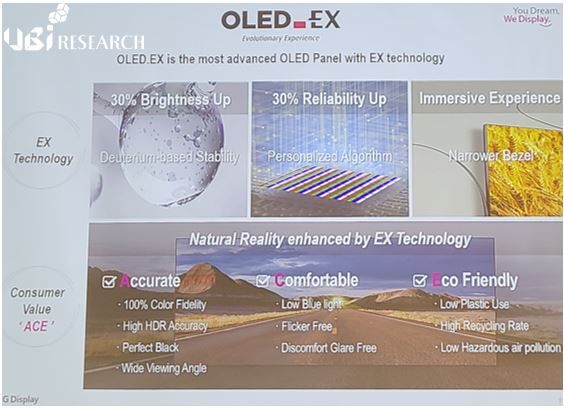
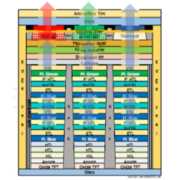
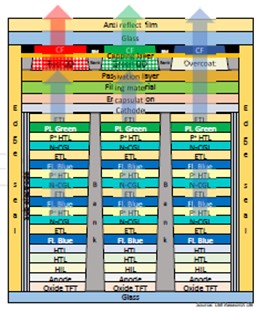
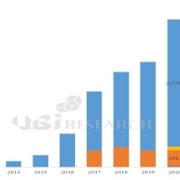
The price of 65-inch premium TV models released from April 2022 was analyzed to have dropped by an average of $800 by October. The price drop is expected to continue for a while because of the Qatar World Cup starting on the 21st of next month and Black Friday on the 25th of November.
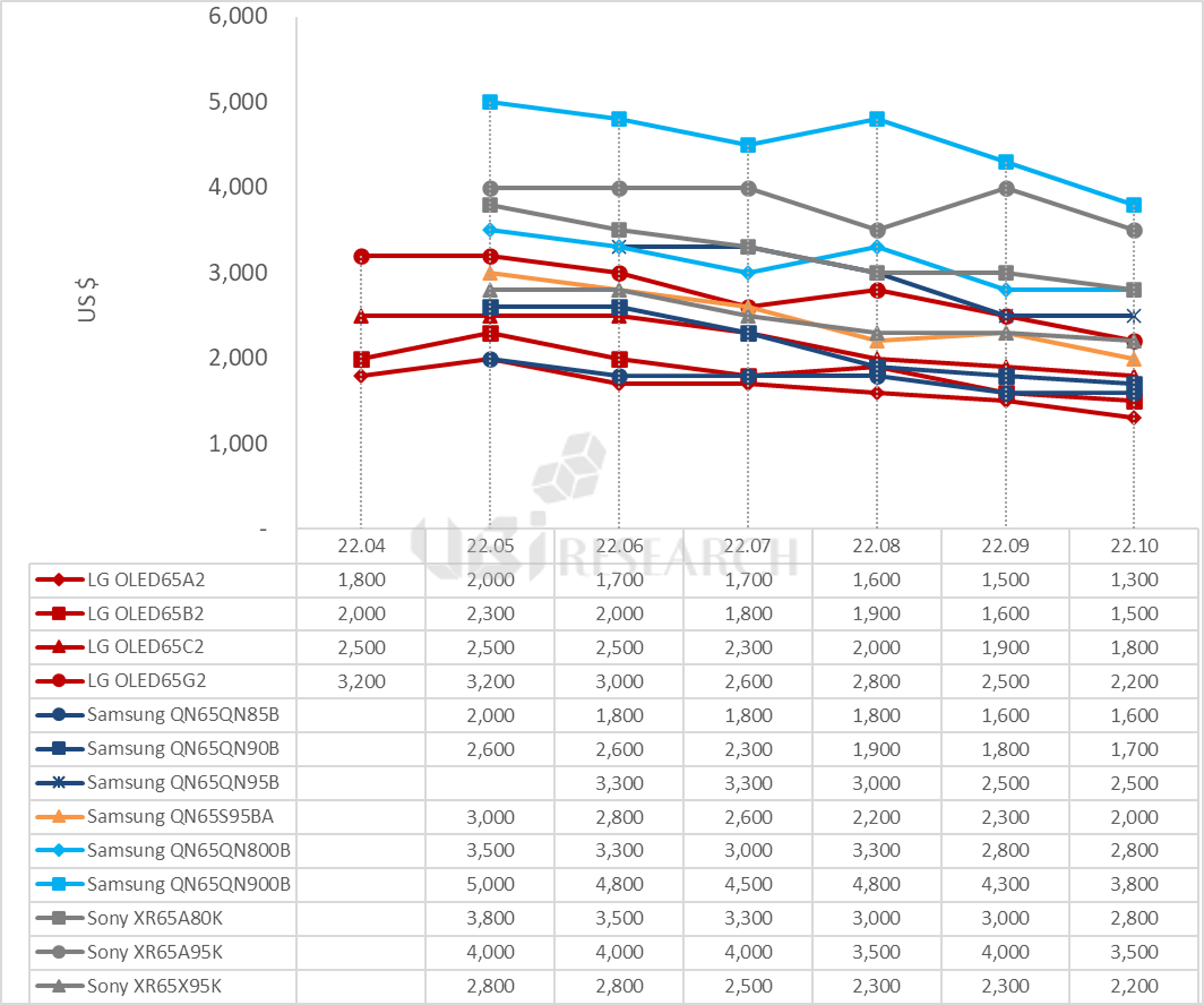
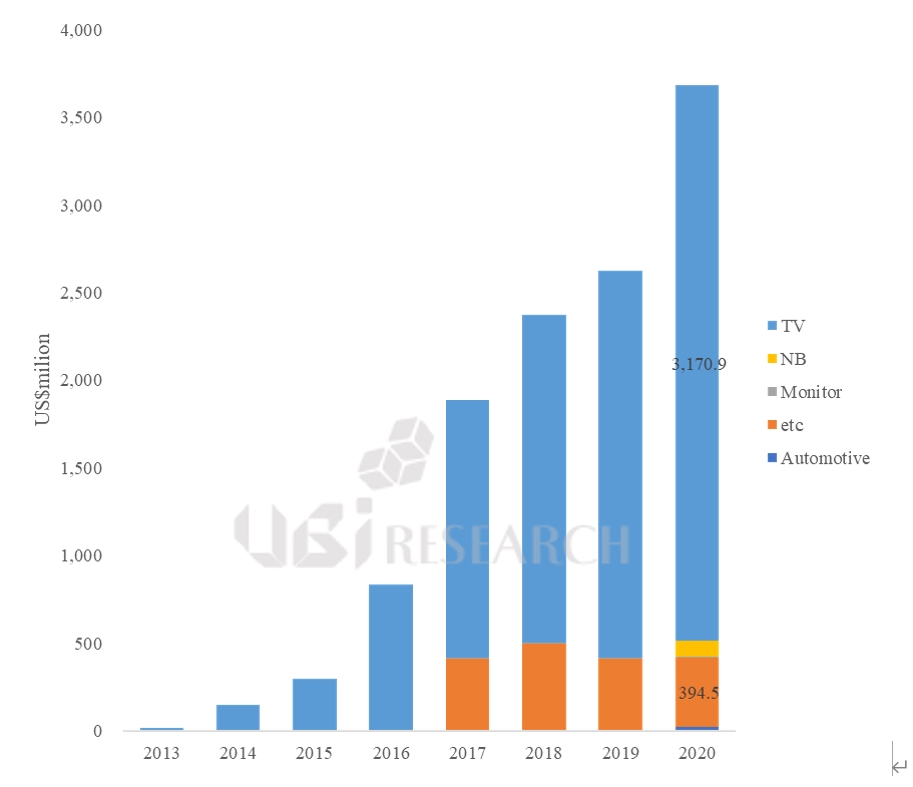
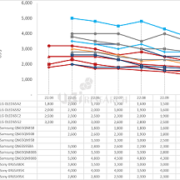
Average prices for 65-inch premium TVs
The prices of Samsung Electronics’ QLED TV and QD-OLED TV, LG Electronics and Sony’s WOLED TV, and Sony’s QD-OLED TV and Mini LED TV were analyzed on a 65-inch basis until October 2022. The selling price of Bestbuy.com was used as the standard, and Sony’s TV was based on the selling price of the official website.
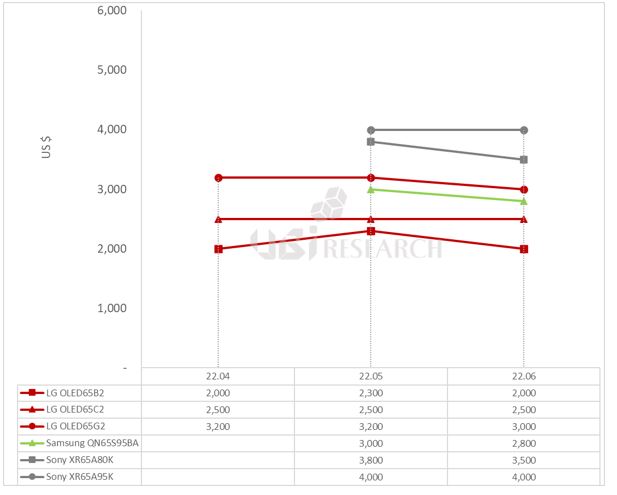
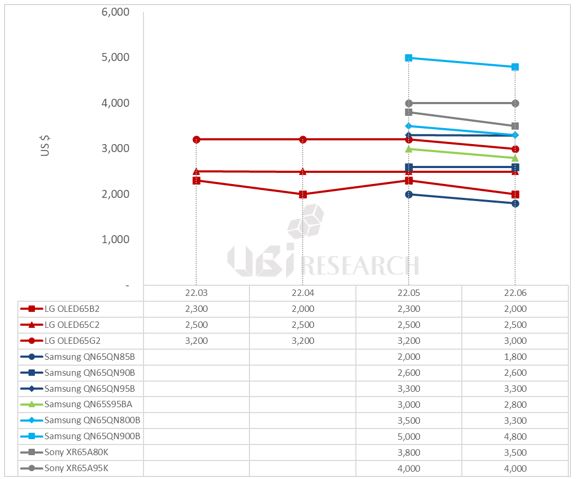
LG Electronics’ WOLED TVs A2, B2, C2, and G2, released in March, were priced at $2,000, $2,300, $2,500, and $3,200, respectively. Samsung Electronics’ 4K QLED TVs 85B, 90B, and 95B cost $2,000, $2,600 and $3,300. 8K QLED TVs 800B and 900B were $3,500 and $5,000. QD-OLED TV, S95B was priced at $3,000. Sony’s WOLED TV, A80K, was priced at $3,800 and QD-OLED TV, A95K, at $4,000. Mini LED TV, X95K was priced at $2,800.
In October, the price of LG Electronics’ G2 model fell by $300, forming an average price difference of $300 per series. Samsung Electronics’ QD-OLED TV, the S95B model, continues to maintain a price difference of $200 lower than LG Electronics’ high-end model, the G2. Sony lowered the price of the WOLED TV A80K by $1,000, the QD-OLED TV A95K by $500, and the mini LED TV X95K by $600.
The higher price of TV, the larger the price drop and among premium TVs, Samsung’s QLED TV, QN90B, had the highest rate of decline at 34.6%. Among OLED TVs, Samsung Electronics’ QD-OLED TV, S95B, had the highest rate at 33.3%.
In terms of price competition, Samsung Electronics’ S95B and LG Electronics’ high-end OLED TV, G2, are competing. Sony’s QD-OLED TV, which had maintained its price range, is also entering the price competition by lowering its price. The prices of Samsung Electronics’ 4K Neo QLED TV series and LG Electronics’ 4K OLED TV series are forming similarly. In Samsung Electronics’ entire TV series, QD-OLED TV is located between 90B and 95B, which are 4K Neo QLED.
Samsung Electronics’ 8K QLED TV, QN800B, has the same price as Sony’s 4K WOLED TV, A80K, and QN900B has a $300 difference from Sony’s QD-OLED TV A95K, leading to consumption of 8K TVs instead of 4K TVs.
With the Qatar World Cup starting on the 21st of next month and Black Friday on the 25th, premium TV prices are expected to continue to decline. Price-competitive marketing by company according to market conditions is expected to be a major variable.
 UBI Research website
UBI Research website
https://ubiresearch.com/en/







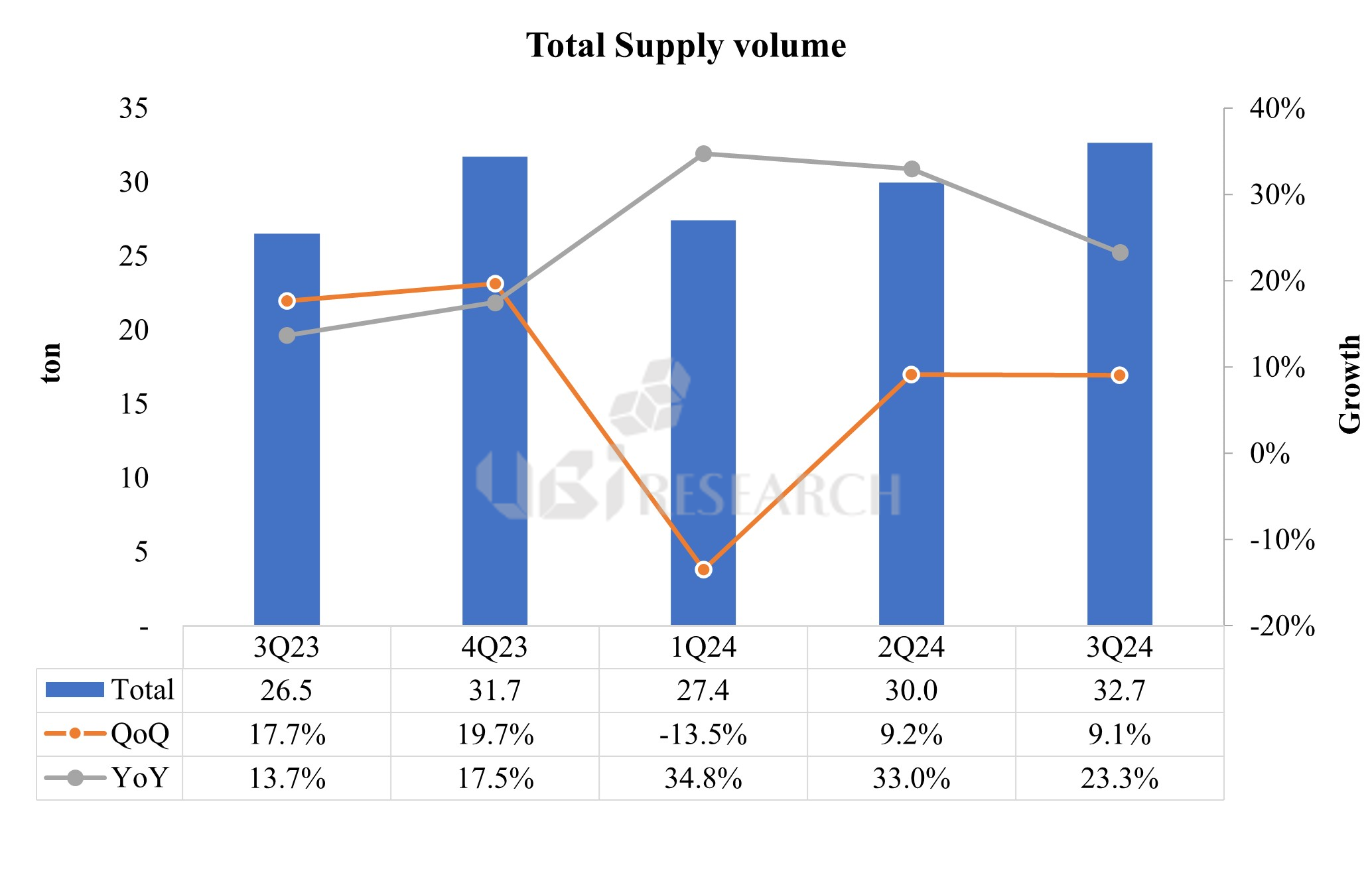
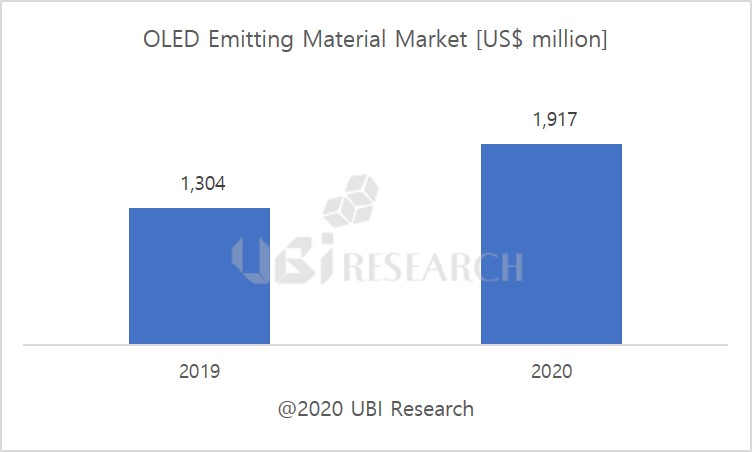
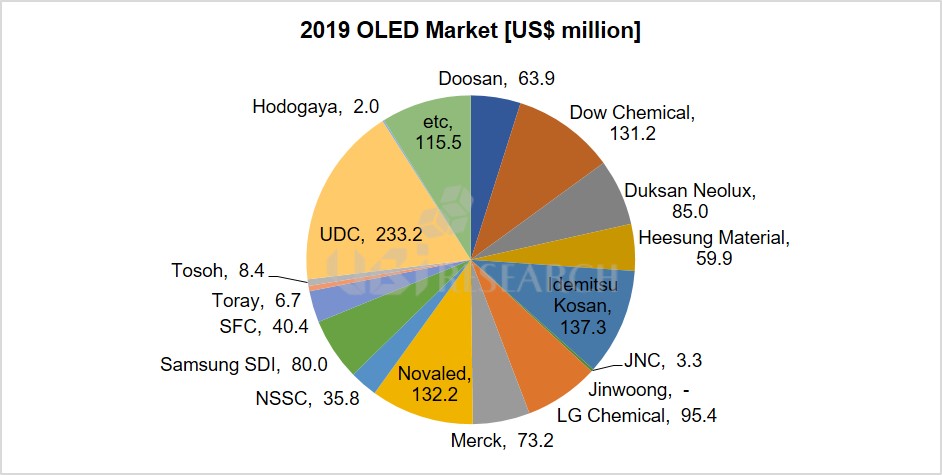
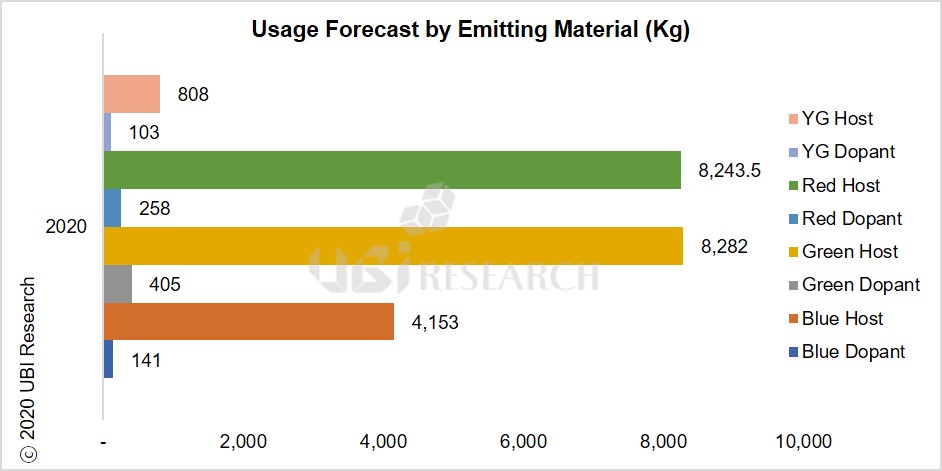
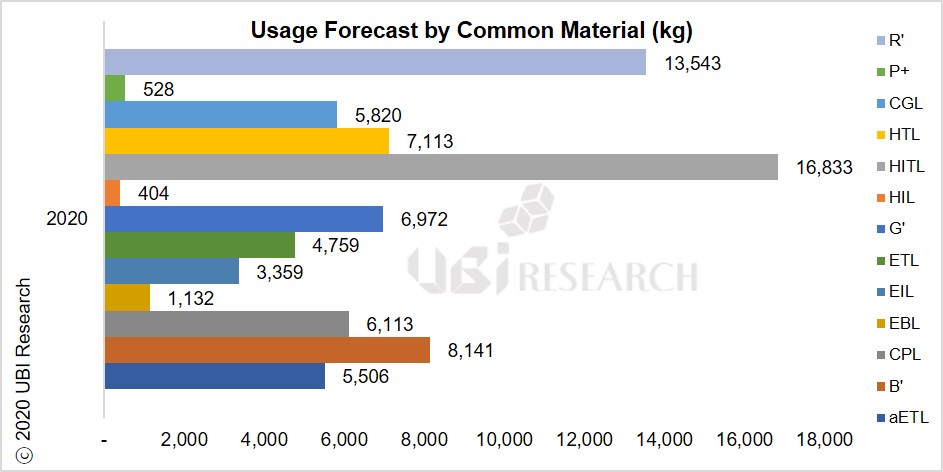
 OLED Emitting Material Market Track Sample
OLED Emitting Material Market Track Sample




 UBI Research website
UBI Research website