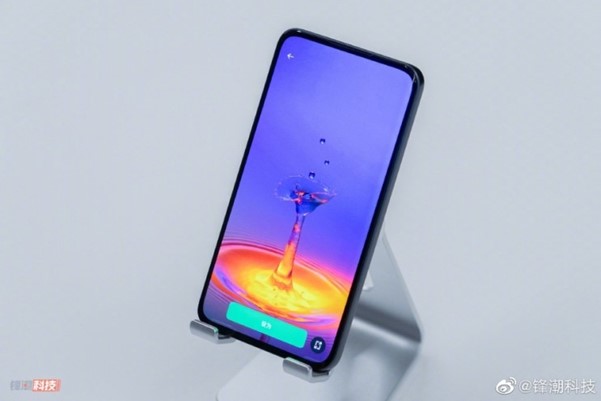
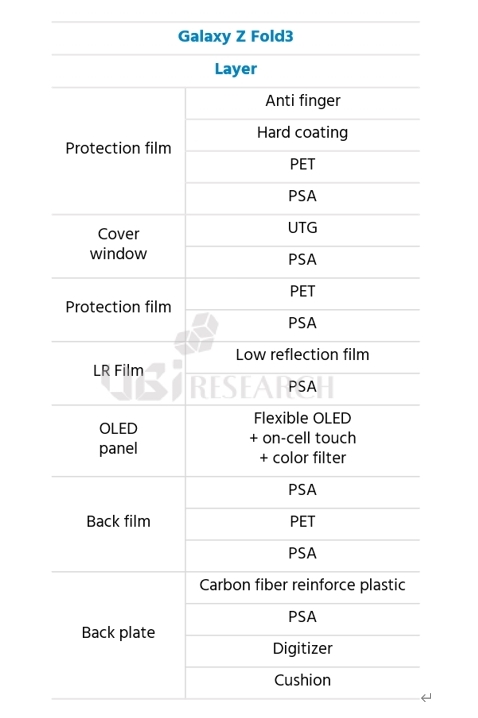
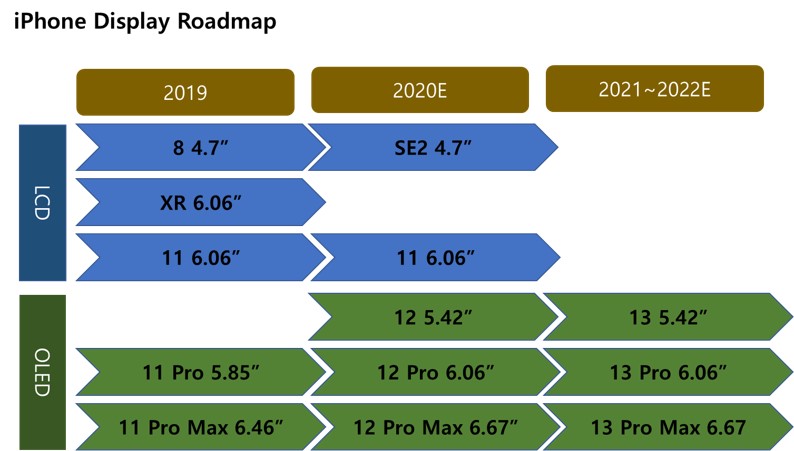
Fewer Notches and More Punch Holes! OLED Smartphones Released in 2022
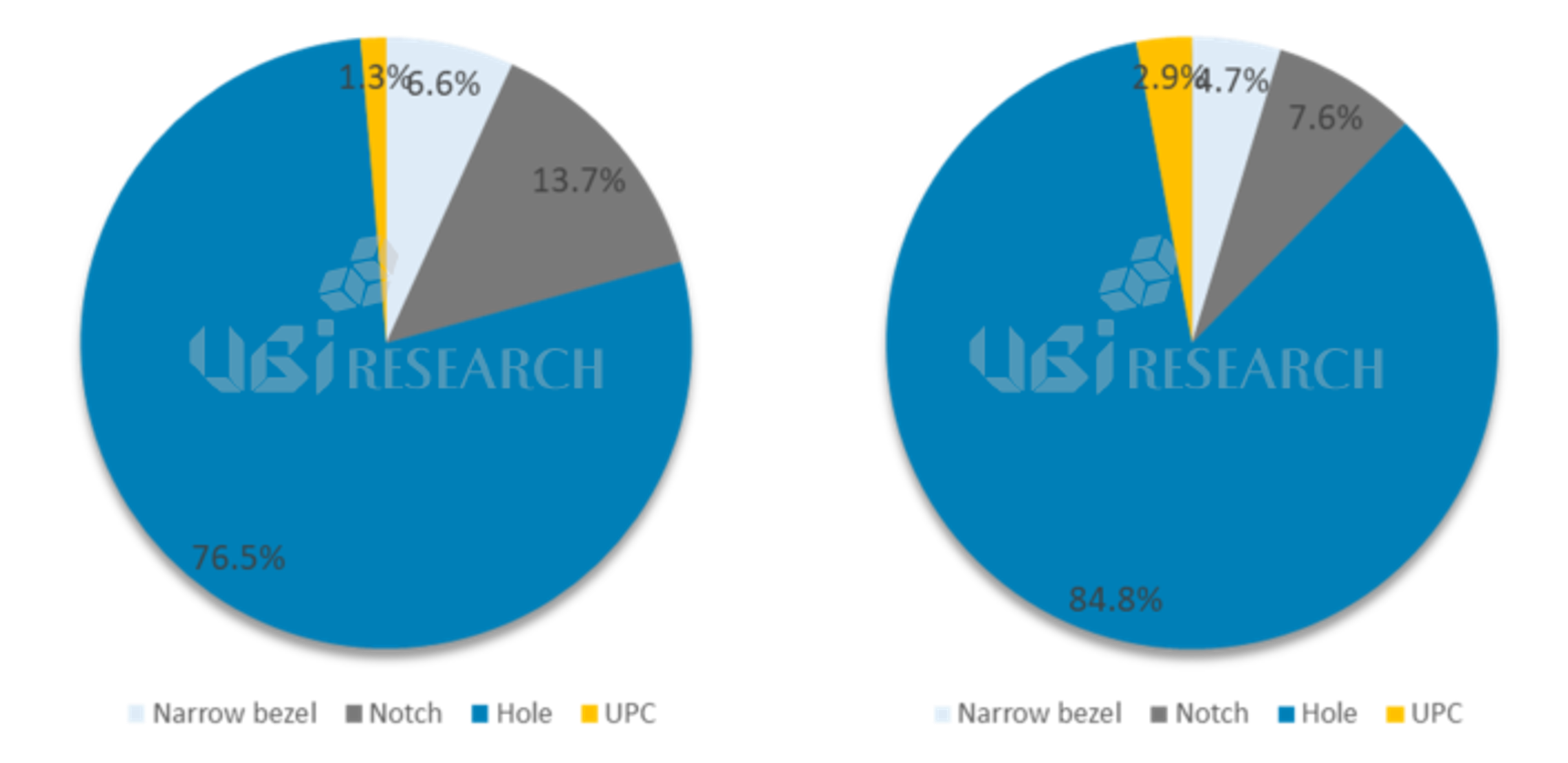
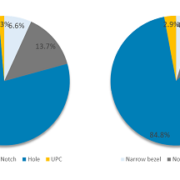
OLED Smartphone Market Share Released in 2021 (left) and 2022 (~3Q, right)
Among OLED smartphones released in 2022, the market share of smartphones with notch and narrow bezel designs decreased by 6.1% and 1.9%, respectively, compared to 2021.
Among a total of 171 OLED smartphones released by September 2022, 145 types of punch hole design, 13 types of notch, 8 types of narrow bezel, and 5 types of UPC (Under panel camera) were released. The total number of OLED smartphones released is similar to that of 2021, but the notch and narrow bezel designs are close to half of those in 2021. On the other hand, the market share of smartphones with punch-hole design increased by 8.3% compared to 2021, accounting for 84.8%.
In particular, Apple applied a punch hole design to the iPhone 14 Pro and Pro Max models instead of the previously applied notch. With Samsung Electronics and Apple, the punch hole design is expected to become more and more of the main technology in the future.
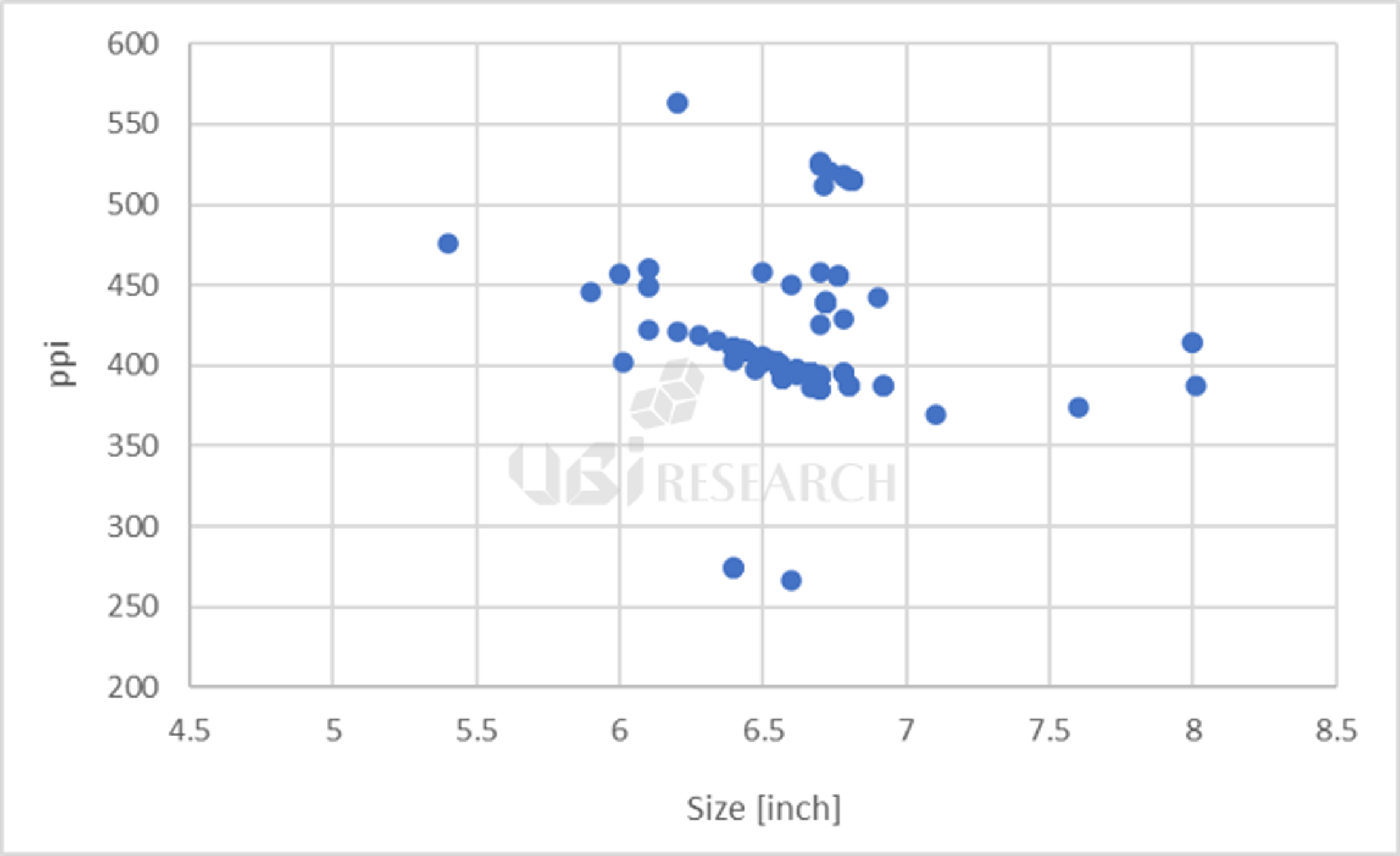
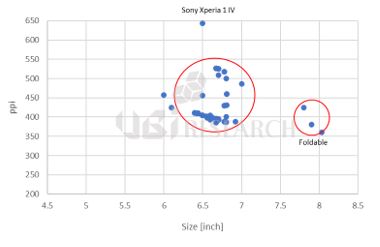
OLED smartphones released by Q3 2022 ppi by size
As for the size, there were 145 types of smartphones in the range of 6.4x to 6.7x, accounting for 84.8% of the market share. In addition, 4 products in the 7-inch range, 3 products in the 8-inch range, and 1 product in the 5-inch range were released. All 7-inch and larger products were foldable phones.
By resolution, 78 products in the 300ppi range and 80 products in the 400ppi range were released. Compared to 2021, the market share of 300ppi products increased by 7.1% and the 400ppi range products decreased by 4.5%. Thirteen products with 500ppi or higher were released and the product with the highest resolution was Sony’s ‘Xperia 1 IV’ at 643ppi.
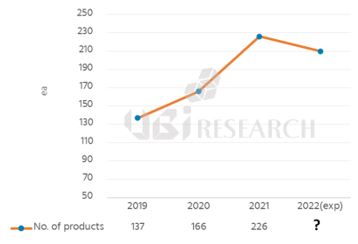
Due to the nature of the fourth quarter, where the number of products released is smaller than in the second and third quarters, the number of OLED smartphone launches in 2022 is expected to be similar to or slightly less than that of 226 in 2021.