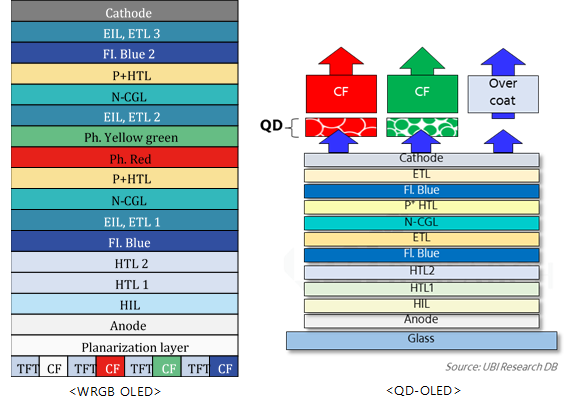
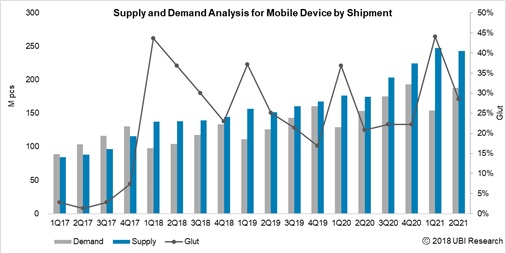
In the 2Q earnings release conference call hosted on the 25th July, Kim Sang-don, LG Display CFO, said, “Looking back at the first half of 2018, the market was in a difficult situation due to the slump in prices, the traditional off-peak season and increased display supply from China. We expected the market conditions to be stabilized in the first half of this year from the bad market condition of the second half of last year, but it has continued to decline more rapidly and steeply. However, with starting the second half of 2018, it has been observing that the price is rising since July owing to upcoming favorable seasonality and customer restocking.”
“Although the market situation has changed favorably in the second half of the year, it is different from the past supply and demand cycle because of the uncertainty of forecasts. Moreover, the oversupply and asymmetric competition in the display market are unavoidable.” LG Display announced that it will maintain its conservative strategy in the second half of the year as the unpredictability is still high.
LG Display’s sales revenue in the second quarter of 2018 was KRW 5,611 billion, decreased by 15% compared to the second quarter of 2017. Operating loss in the second quarter of 2018 recorded KRW 228 billion. This compares with the operating loss of KRW 98 billion in the first quarter of 2018 and the operating profit of KRW 804 billion in the second quarter of 2017. The company suffered a large deficit due to a continued and steep decline in panel prices and lower demand in panels following the previous quarter. Although the shipment was increased by 2% QoQ, the selling price per area (m2) was decreased by 4%.
As a positive indicator, the TV panel price fell sharply, but the overall panel price decline was only 1% due to the competitive position of OLED panels. The market is anticipated to turn into positive situation in the third quarter, compared to the first half of the year, since panel shipments are expected to increase with the orders to restock the inventory.
LG Display, which is currently conducting both LCD and OLED business with small and medium sized panels and large area panels, mentioned clearly about its future strategic direction including the direction for the second half of the year as “concentrating on OLED business and focusing on high value of LCD business” in this conference call.
LG Display announced that it will focus more on differentiated LCD features and technologies in the IT sector such as narrow bezel, IPS borderless, and oxide technology, as well as high-value-added products such as larger-size TV panels and commercial displays, considering that a structural oversupply in panels and fierce competition among display makers are expected to continue down the road.
In addition, LG Display will achieve a turnaround to profit in the OLED TV sector in the third quarter of 2018. By making its final decision to invest in its Gen 10.5 OLED panel production line in Paju, Korea, and by starting mass production in the latter half of 2019 at its Gen 8.5 OLED production line now under construction in Guangzhou, China, LG Display will accelerate the expansion of the global large-size OLED market. Furthermore, additional production facilities for OLED 8.5 generation are known to be considered with the plan that the rationalization of LCDs during the year is also to be implemented although there was no direct mention of the timing and specific lines. For the plastic small and medium-sized OLED panel business, which is experiencing difficult times, compared to large area OLED, for which LG is expanding the production capacity in response to increasing demand, it said that they are preparing for future markets with the necessary strategic technologies with the emphasis of mobile and automotive markets. The E6-1 line, which has been mentioned as a production plant for Apple, is expected to begin mass production in the fourth quarter of this year, revealing the possibility of a possible supply of display to the iPhone OLED model in 2018. In addition, demand for OLED panels is increasing in the automobile market, and it is expected that full-scale business will start in the second half of next year. At the current order backlog, it is confirmed that OLED panels are in the late stage of about 10%. This means that much of the work has already been done. Finally, LG Display is well aware of the lack of funding and funding shortfalls over its competitors in relation to its future preparations. The company plans to reduce its capex by about 3trillion won by 2020, with a substantial portion of depreciation and amortization It is possible through internal working capital management and it plans to borrow the rest. LG Display confirmed that it has not reviewed the rights issue several times in the market, and LG Display has thoroughly prepared a variety of OLED portfolios, revealing its commitment to success by differentiating it from its competitors in the area of latecomers.