How far has QNED completed?
The reality of QNED (quantum dot nano-rod LED), which Samsung Display is preparing as a next-generation display, has become clear.
As a result of analyzing 160 patents applied by Samsung Display, it was confirmed that the structure constituting the QNED has already been completed, and that the only remaining task is to keep the number of nano-rod LEDs arranged in the light-emitting pixel constant.
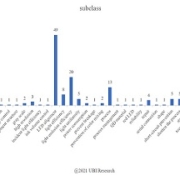
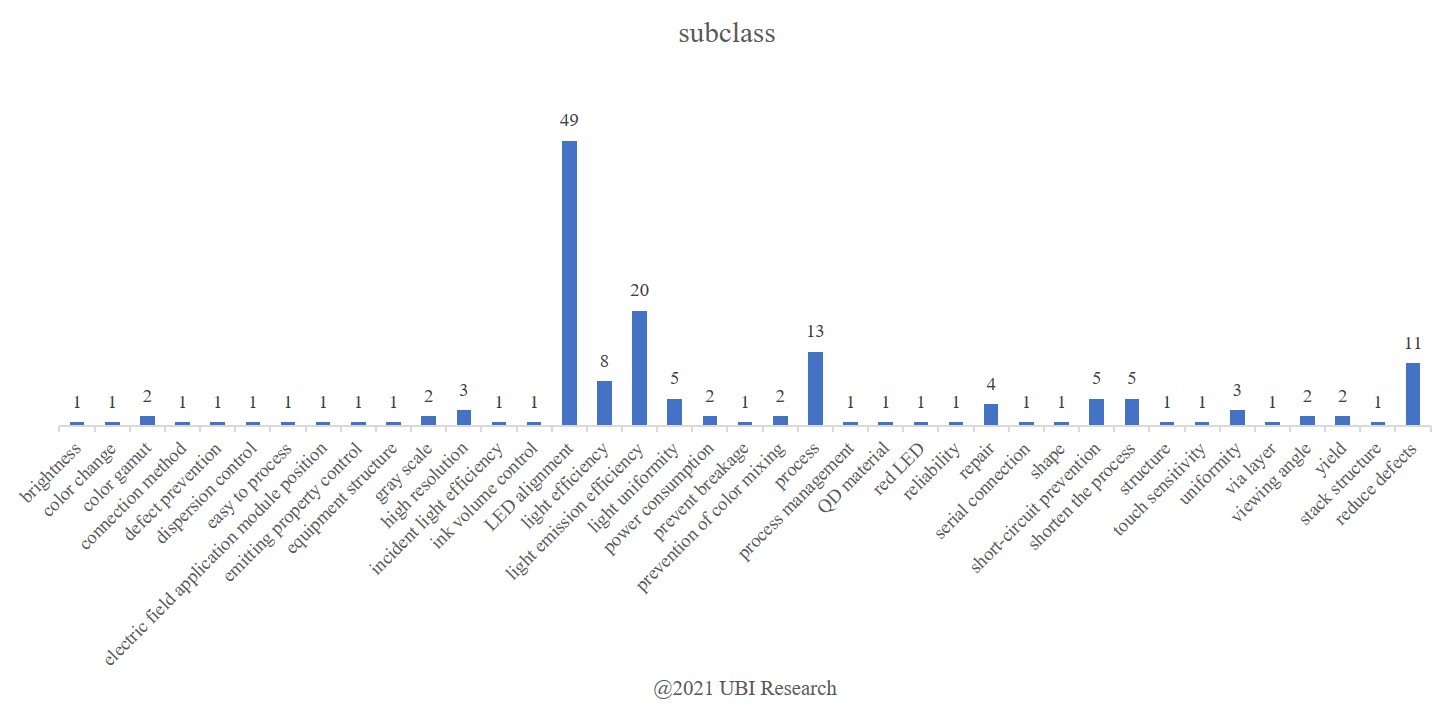
As a result of classifying the contents of each patent according to the purpose of the application, a total of 39 types were found, with 49 cases related to device arrangement being the most. The following is 20 cases to improve the light efficiency.
The number of aligned nano-rod LEDs per pixel, which determines the yield and image quality characteristics of QNED, is determined by the distribution of LEDs in the ink, the number of LEDs injected into the pixel, and the alignment ratio of the injected LEDs.
If the distribution of the number of nano-rod LEDs per pixel is different, there is a change in the voltage applied to each pixel, resulting in a defect.
It has been confirmed that Samsung Display has already developed a method for making the number of nano-rod LEDs per pixel constant and an algorithm that can make the luminance uniform even when the number of nano-rod LEDs is different.
In the “QNED Technology Completeness Analysis” published this time, it was written as the contents of the previous report published through analysis of 94 patents and 66 newly added patents. It was analyzed and recorded.
In this report, QNED patent numbers, classification tables, and quantitative analysis data that have not been disclosed before are provided in Excel.