Dr Choong Hoon Yi, UBI Research Chief Analyst, ubiyi@ubiresearch.co.kr
Korean TV industry, according to recent reports by media, is showing a red light not being able to escape the deficit structure.
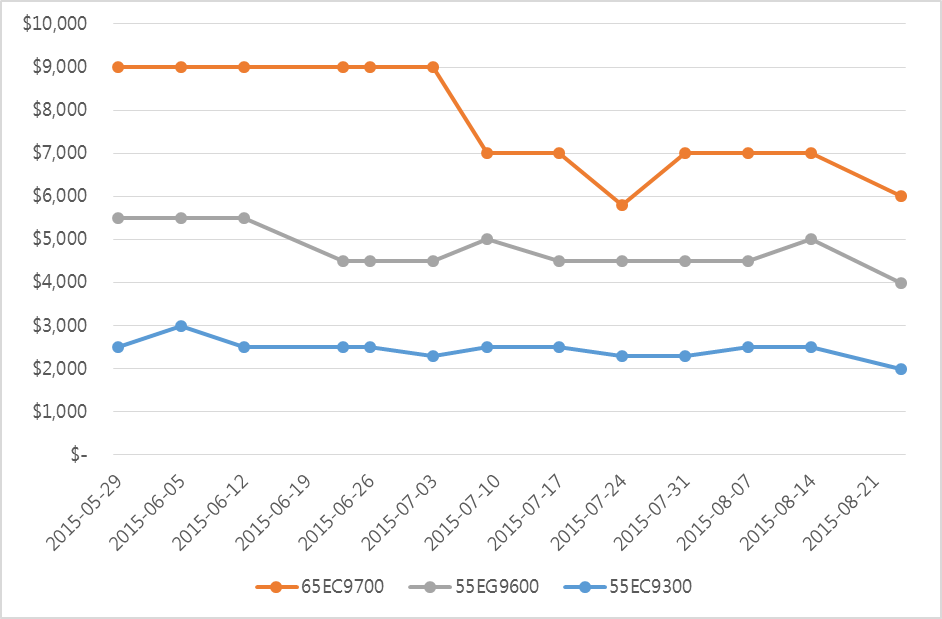
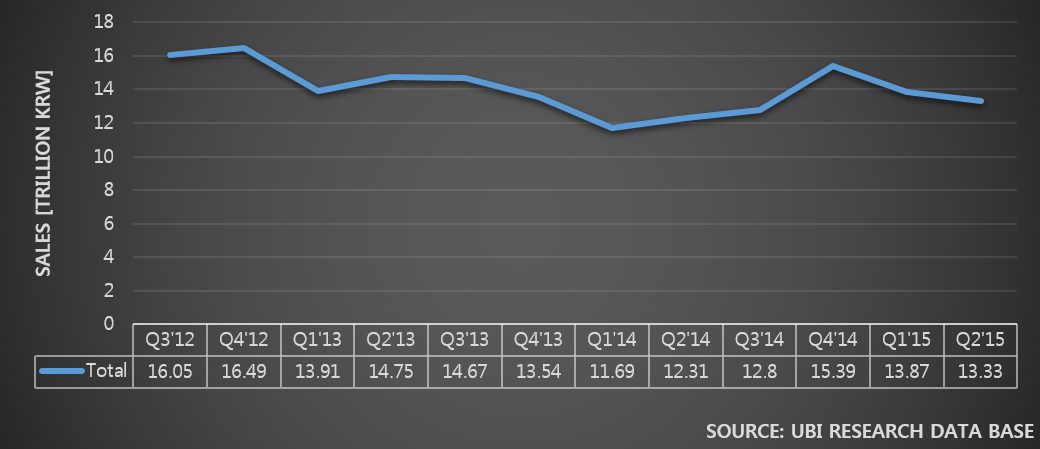
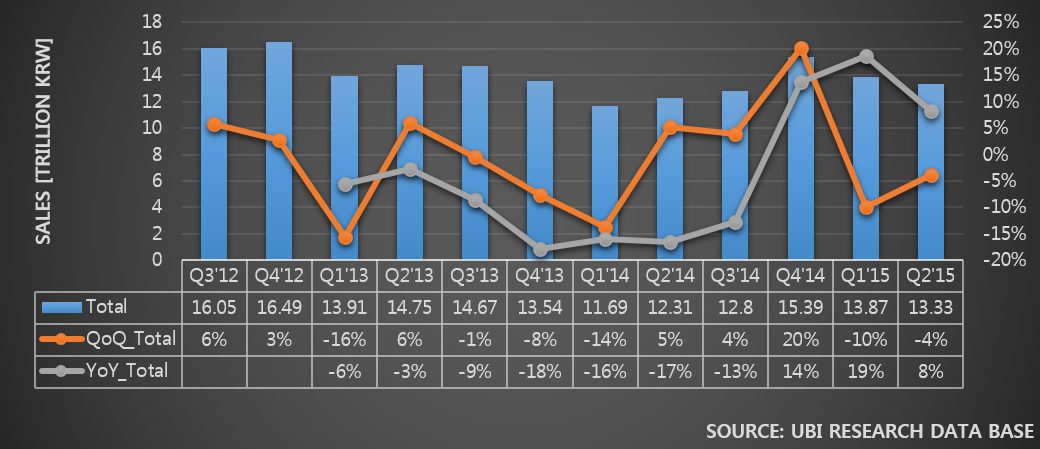
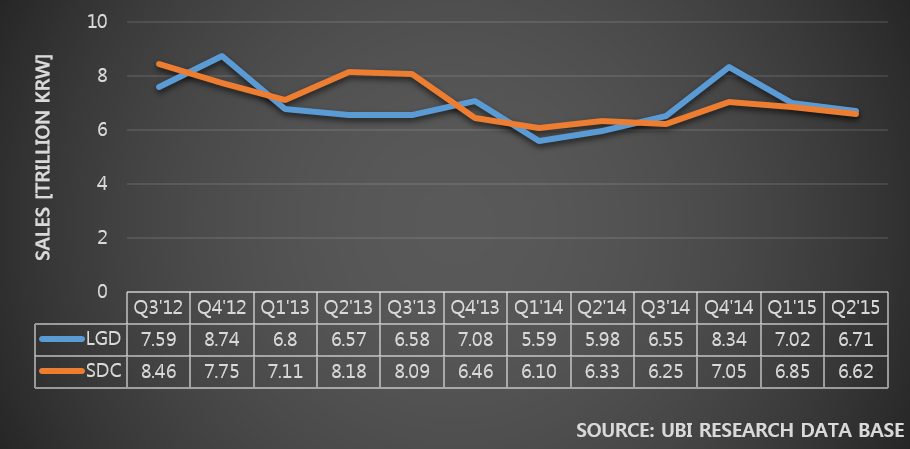
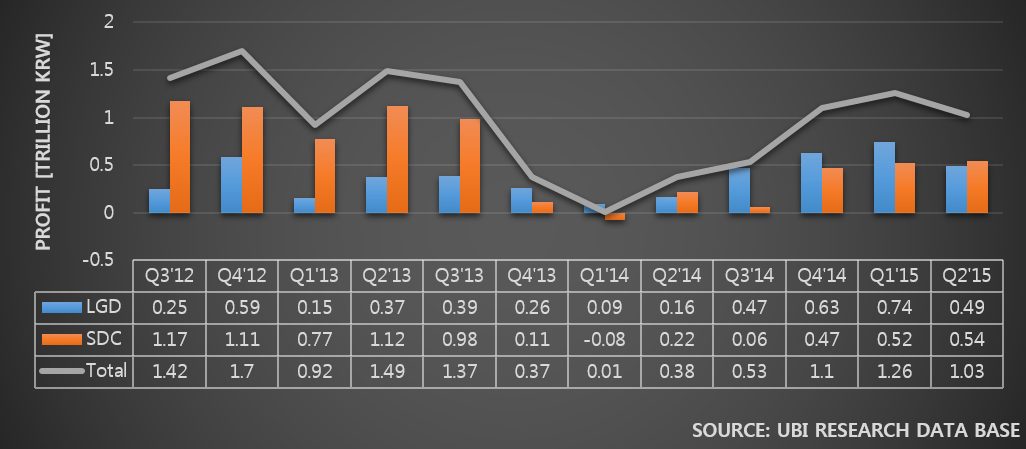
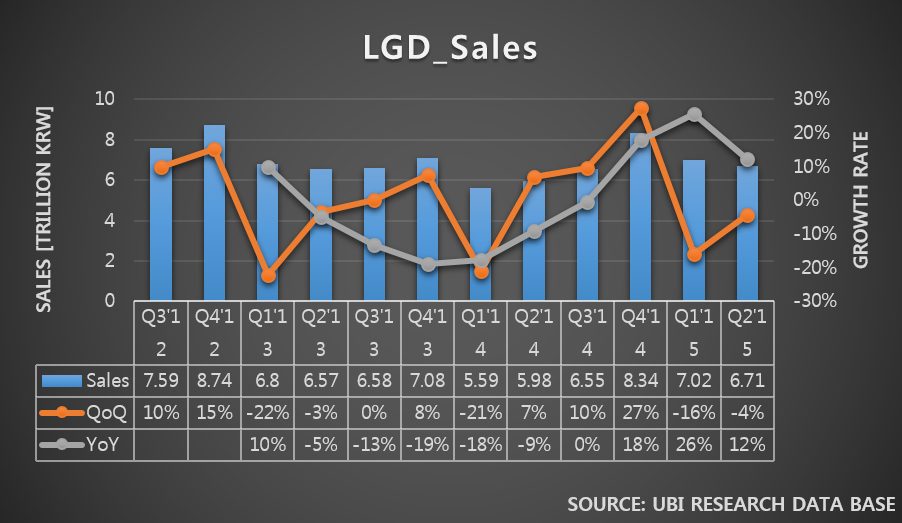
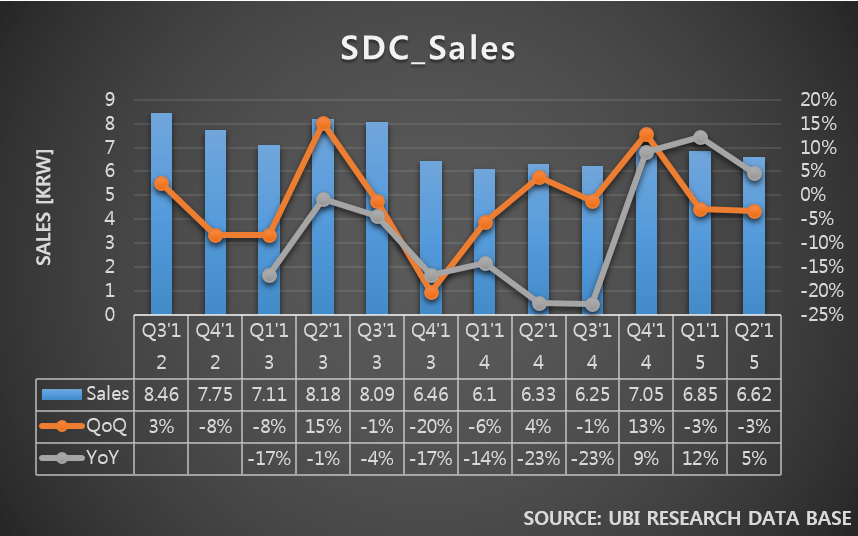
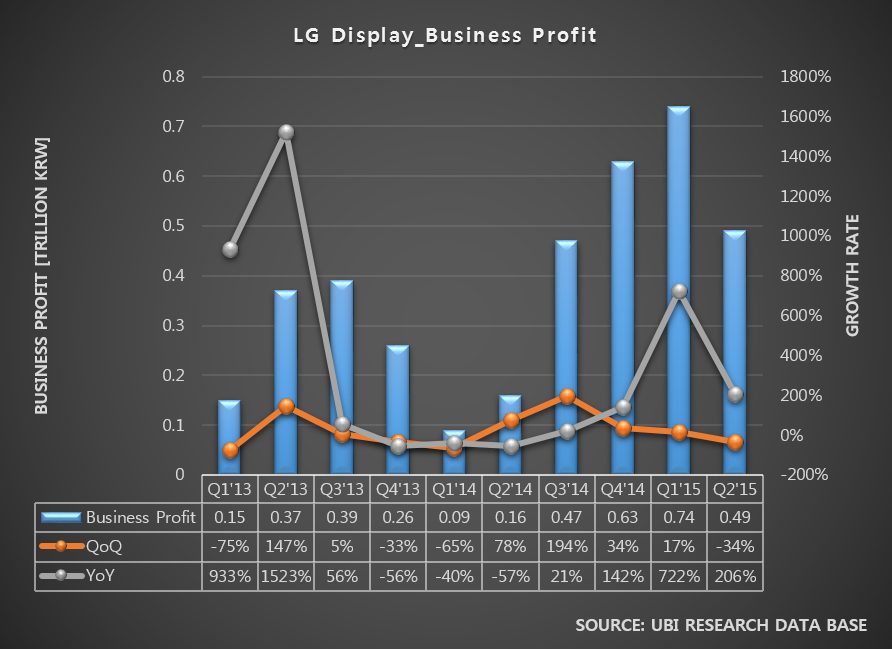
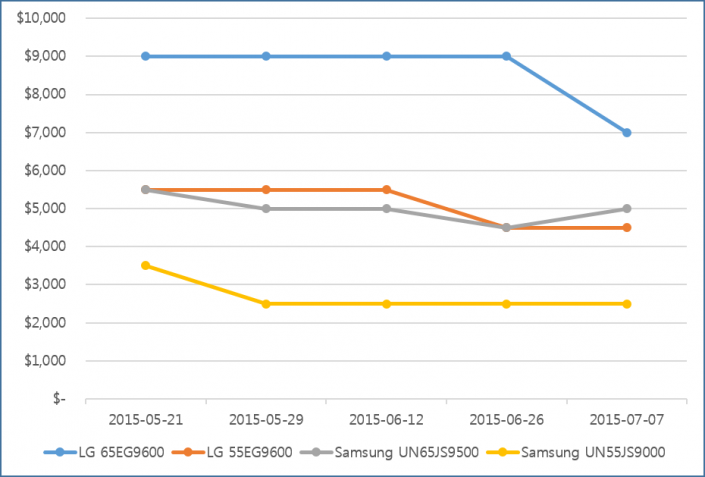
Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics possess high market share in costly premium TV market. However, in 30inch grade market, the two companies struggle against economically priced sets. In order to maintain sales, Samsung Elec. and LG Elec. are managing diverse product portfolio but business profit keep falling. Due to this, LCD panel stocks produced by Samsung Display and LG Display are steadily increasing.
LCD panel business is sinking into a pit.
What is the reason that Korea’s LCD TV and LCD business values can only become worse?
This can be forecast from looking at Japan’s TV and LCD business. Until the early 2000s, Japan was one of the leaders in electronics. However, Japan’s TV business is gradually dying out. Japan’s leading companies, Sony and Panasonic’s TV business began to be deteriorate because of Korean mid-low price products. In succession, Sony ended up spinning off the TV business, and Panasonic stopped TV business other than for domestic supply. Korean TV companies began to dominate the market. However, only a few years since then, Korean TV industry is losing commercial value, pushed aside by mid-low price products manufactured by China and others.
Second is display investment. As Japanese TV industry began to crumble, Japanese display companies had no choice but to stop the investment. The companies could not see a way to make profit through investment even if TV market grew as client companies’ panel purchasing power fell. Korea is the same. Samsung Elec. and LG Elec.’s TV business profitability deterioration led toward Samsung Display and LG Display’s halting the investment. On the other hand, Chinse display companies began Gen10.5 line investment. TV industry relies on assembly business and business network and therefore initial investment cost is low. In comparison, display industry is high risk as it requires large scale investment from early stages. If the business profit falls without investment cost return, companies face great loss and business closure is also not easy.
The third reason that Japanese TV companies are dying out is because they could not produce premium TV. Sony, which lost its competitiveness in LCD TV, tried to strengthen its market leadership through 4K TV. However, the brand value was already down and with the lack of marketing value, Sony easily gave up the market to companies in pursuit such as Samsung Elec. and LG Elec. LCD TV already had no difference in quality whether it was produced by a Korean or Japanese company, and brand value order had switched. LCD TV quality produced by Chinese companies is already reached the top. They are no longer companies who produce cheaper knockoffs. Furthermore, LCD panel production technology of Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and China can now be deemed equal.
The final reason that stops Japanese TV business from securing market is that they failed to suggest differentiation point in premium TV. Fundamentally, differentiation is not possible for LCD TV. The biggest differentiation factors in the current TV market are picture quality and design. Any company can produce thin LCD TV and curved LCD TV. Panel size, resolution, and QD-LED using color gamut that LCD can actualize can no longer be differentiated technology. The difference of LCD panel and TV manufacturing technology between Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and China is already within a year. No matter what kind of product is released, market control has one year of expiration period. Considering the promotion period required in the market is approximately 6 months, the period where profit can be made is shortened even further.
So what is the solution for the Korean TV industry to survive?
As I have mentioned dozens of times for several years, what is left is OLED TV. What LCD cannot do in terms of picture quality and design, with OLED it is possible. Therefore, only the non-LCD products can enjoy the key factors of differentiation in premium TV market.
Existing premium TV is IPTV, a market that Japanese TV companies have been pursuing since early 2000s. Internet connection is possible through TV and allows for exchange of information in both directions. The basic concept of IPTV is watching TV while searching the information on TV via internet. But how useful is this concept at present? The usefulness of IPTV is becoming increasingly low as smartphone is used to search information, use the internet, and even watch TV. With no reason to use the internet via TV, TV companies should seriously consider whether TV with high white brightness is really needed. Rather than white TV with high brightness, it is time to place more importance in the functions of the TV itself. TV screen only uses 20-30% of full white brightness. Films, with outdoor shooting, falls under 20%, and for contents shot at night, black is more important.
Considering ‘blackness’ and design, anyone can find where the solution lies. If the foolish notion of trying to make OLED as bright as LCD is abandoned, there is hope.

LG OLED UHD TV, SID 2015

Samsung OLED UHD TV, IFA 2013