Dark clouds are approaching Korean industry by the corona virus that has been blown since the beginning of the year. Wuhan, the birthplace of the corona virus, is badly affecting the Chinese display industry because it is a key place where Chinese display makers are building large production bases.
Wuhan and other plant set-ups are experiencing difficulties due to the lack of manpower needed to build the line. At the same time, the utilization rate of the entire supply chain in China is falling sharply, as the labor force of parts and materials manufacturers in China is delayed to return to the factory. In the smartphone industry, the center of the OLED industry, iPhone production is affected in the first quarter. Foxconn’s factories, which produce iPhones in Zhangzhou and Shenzhen, China, are operating at 50% at end-February. This is because manufacturing workers are returning to the factory late. Companies such as Huawei, Xiaomi, Oppo, and Vivo are also hampering smartphone production due to delays in parts procurement.
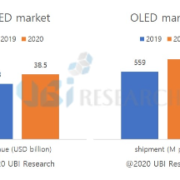
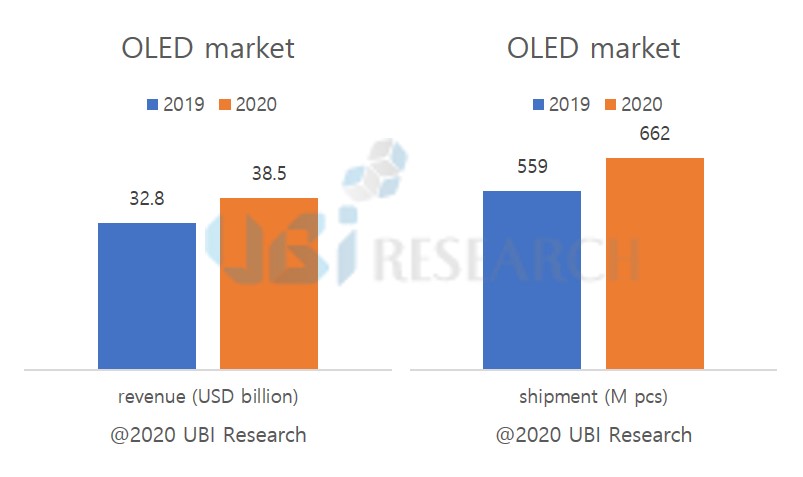
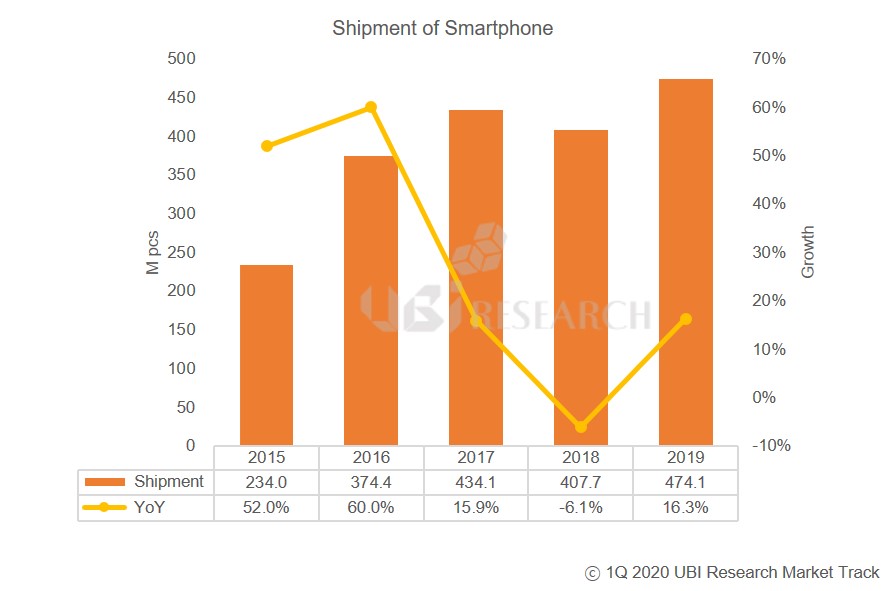
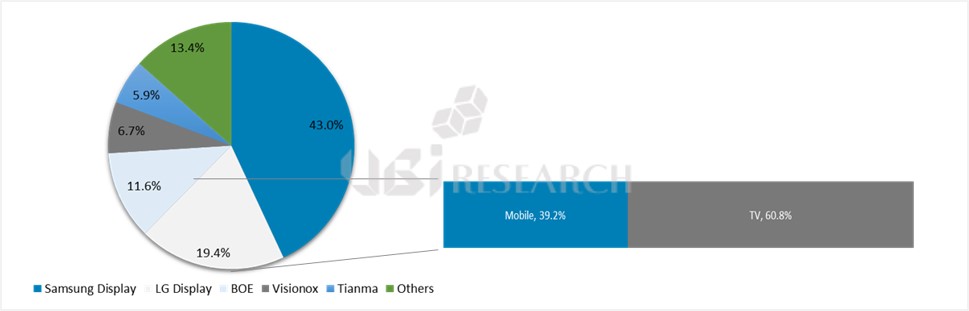
Nevertheless, the production of OLED smartphones is not much affected yet. First, Samsung Display’s panel production plant, which accounts for 86.3% (2019) of OLED shipments for smartphones, is located in Korea, while the module plant in Vietnam is not affected by China. In addition, the supply chain has no effect as most of the material production bases that make up OLED panels (including modules) are also in Korea.
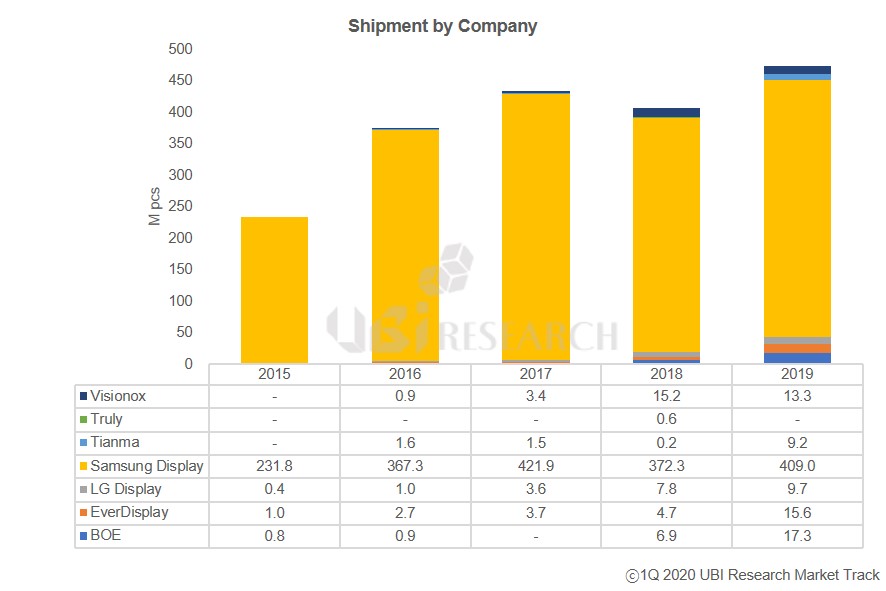
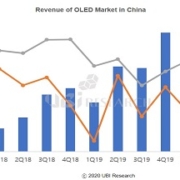
Samsung Display’s OLED production for smartphones in January and February totaled 48 million units, less than 2 million units compared to 50 million units shipped in the same period in 2019. Of these, 14 million and 17 million units were supplied to Chinese smartphone makers in 2019 and 2020, respectively. This year, more than 3 million units are shipped. So far, Samsung Display’s OLED business is not affected by the corona virus.
The total market share of Chinese OLED panel makers in 2019 is 11.7%. By February, the panel utilization rate of Chinese OLED panel makers was maintained at 80%. The impact of factory operation due to lack of manpower is about 20% because most of the display manufacturing industry is driven by automated facilities. Chinese OLED makers import most of the major materials, including light emitting materials, from Korea and Japan, so they are hardly affected by the corona virus.
The parts procurement status of smartphone makers in China affects the market. If Chinese suppliers, including Huawei, fail to procure parts in China, smartphone production will be hampered. However, as Samsung Display’s OLED production for China is progressing smoothly, Chinese smartphone makers have a strategy of maintaining OLED smartphones, which are expensive brands.
In addition, the first quarter is the off-season with the lowest shipment season, so even if it is difficult to operate a smartphone manufacturing plant until March, the impact on the overall market is about 10%. After the second quarter, if the corona virus subsides, demand can resume.
The problem is from March. China’s corona virus has slowed down, but South Korea has been expanding since the last week of February. There is someone has a virus at Samsung’s Gumi smartphone manufacturing plant. In addition, the Vietnamese authorities, concerned about the influx of South Korea’s virus, refused to visit Koreans, which may make it difficult for the headquarters to properly deal with problems with Samsung Display’s module plant management in Vietnam.
Most important of all, the corona virus is spreading all over the world, and economic activity is severely reduced. In China, the entrance of the apartment is blocked, so it is difficult to bring TV. The Chinese TV market is shrinking. Many people are refusing to go out because they are concerned about a corona virus infection, so fewer people visit a store and buy a smartphone. Consumer sentiment is falling significantly.
Assuming that the corona virus crisis will end in March in Korea and China, the impact of the smartphone OLED industry on 2020 is estimated to be about 5%, but if it is prolonged, it may be adversely affected by more than 10%. Assuming that the corona virus crisis will end in March, the impact of the smartphone OLED industry on 2020 is estimated to be around 5%, but if it continues until the first half of the year, it could be adversely affected by 10%.
The OLED business for TV is slightly different. LG Display’s factories that produce exclusive OLED panels for TVs are located in Paju, Korea, and Guangzhou, China. The Paju plant is not disrupted at all. Like OLEDs for smartphones, parts and components are mostly supplied by Korean and Japanese companies, so Paju factory is not affected by China.
The problem is the Guangzhou plant. LG Display has been expected to produce panels since September 2019, but its supply has been delayed due to poor panel lifetime. LG Display has begun production of panels again this year and is undergoing product tests from customers. Recently, however, the corona virus has begun to spread in Korea, making it difficult for Korean engineers to go to Guangzhou. Even if the corona virus disappears in the first quarter in China and the factories operate normally, it may take some time before the panel is supplied from the Guangzhou plant.
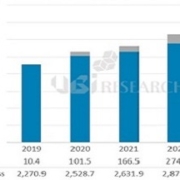
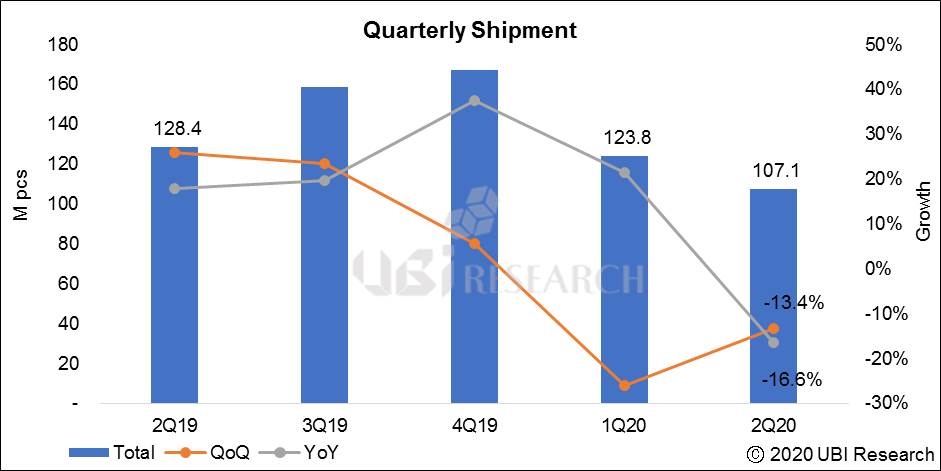
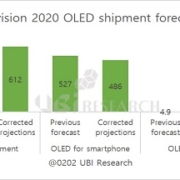
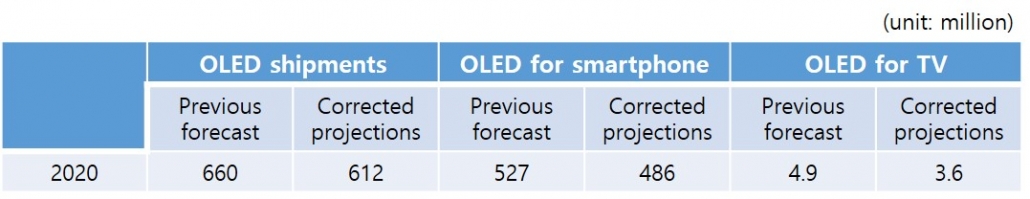
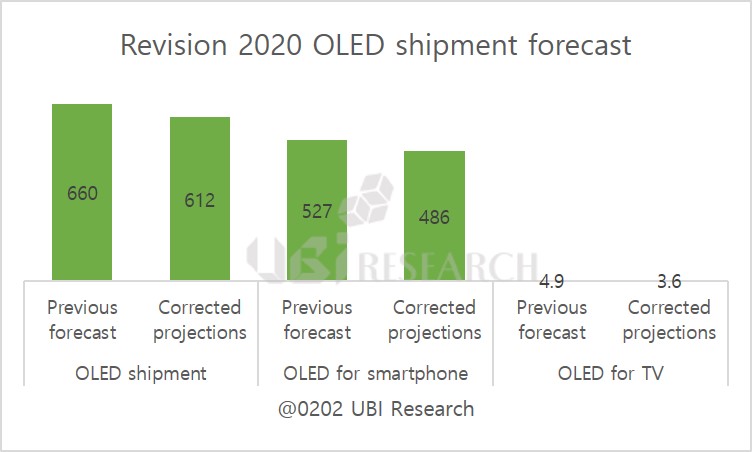
According to Ubi Research’s OLED market track, the 2020 forecast is 4.95 million units without considering the corona virus situation, of which 750,000 OLED panels for TV can be produced by LG Display in the first quarter. If the 55-inch production volume is large, up to 800,000 units can be produced. Since the data were prepared in anticipation that panels produced at the GuangZhou plant will be available from the second quarter, LG Display’s panel supply is expected to be 1.4 million units in the second quarter.
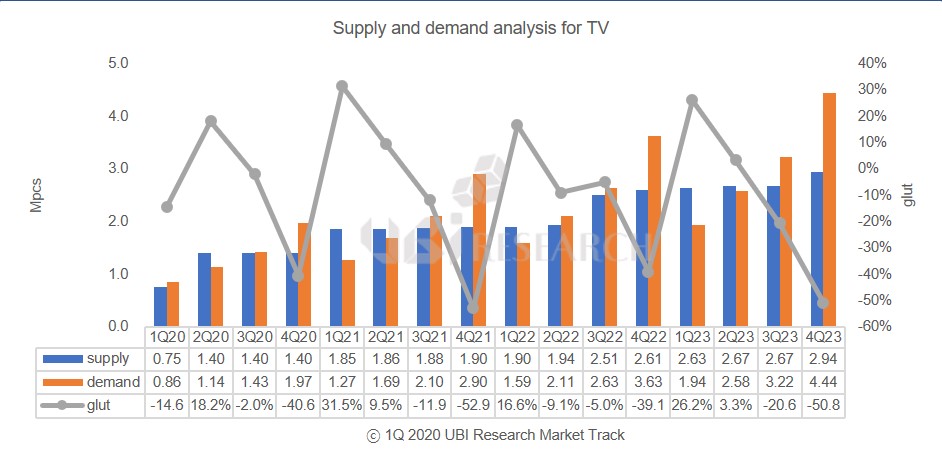
However, it is possible that production will be delayed after May if the customer’s quality certification of panels produced at Guangzhou plant is delayed due to the Korean coronavirus rather than the Chinese coronavirus. In that case, the annual TV panel production could be reduced by about 200,000 units, which is expected to decrease by 4% from the estimated total. However, if the corona virus is prolonged by June, it can cause up to 10% of adverse effects. The market should consider 500,000 fewer than expected.
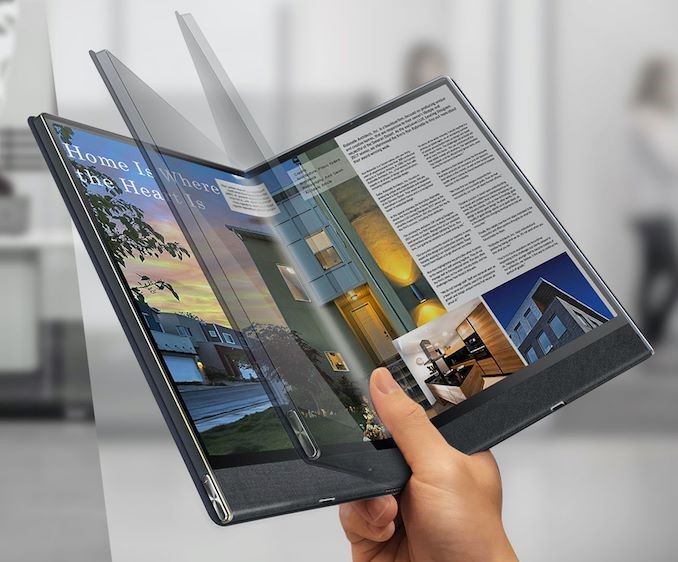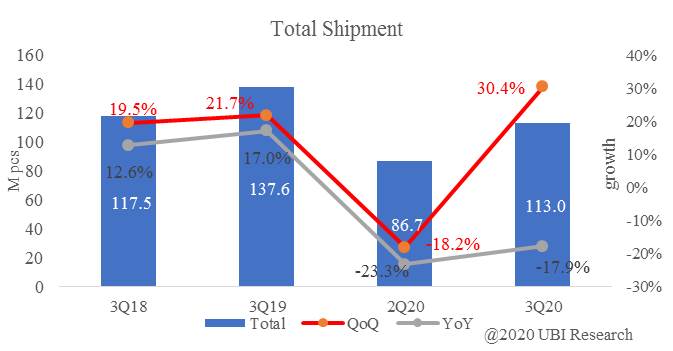























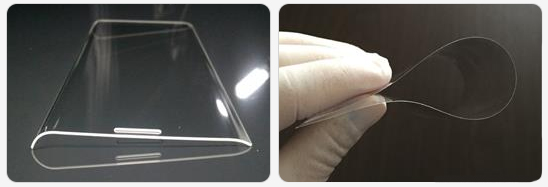

















 The tablet can be folded in half with a foldable OLED and a zero gap lay flat hinge. Fold in half to use it like a notebook. Attach a keyboard to make it easier to use. This product can use stylus.
The tablet can be folded in half with a foldable OLED and a zero gap lay flat hinge. Fold in half to use it like a notebook. Attach a keyboard to make it easier to use. This product can use stylus.