Why did Apple choose LTPO?
- Utilizing high refresh rate and reducing power consumption by up to 20%
- but, 30% more complex process
LTPO (Low Temperature Poly-crystalline Oxide) is an Apple’s technology made by combining LTPS (Low Temperature Poly-Silicon) and Oxide (oxide semiconductor, mainly IGZO) TFT technology. It is characterized by further improving power efficiency by using LTPS with fast electron mobility and oxide with less leakage current.
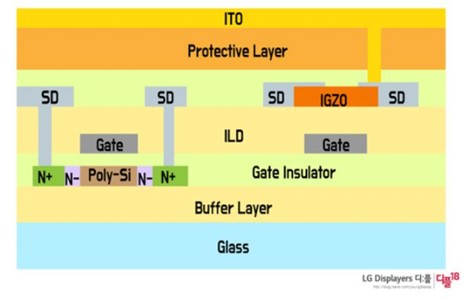
LTPS TFT with fast electron mobility is applied as a driving role, and oxide TFT with low leakage current is applied as a switch.
LTPO was first applied to smart watches before smartphones. The first device to be applied is the Apple Watch Series 4, released in 2018, and was supplied exclusively by LG Display. Samsung Electronics also applied LTPO to the Galaxy Watch Active 2 in 2019.

Apple Watch with LTPO applied

Galaxy Watch Active 2
LTPO technology, which is characterized by low power, is suitable for 5G smartphones that consume more power than existing LTE and is in high demand from major smartphone manufacturers. Samsung Display launched the Galaxy Note 20 Ultra, the first smartphone to which LTPO technology was applied.

Galaxy Note 20 Ultra with LTPO applied
It is expected that Samsung Display will dominate the market as it is leading in technology of LTPO OLED panels for Smartphones, and as a latecomer, LG Display is known to develop panels to be applied to the iPhone, which is scheduled to be released next year.
LTPO technology does not only have the advantage of low power. Because masks are added during the process, the unit price is increased due to the complexity of the process. Manufacturing methods are completely different from existing LTPS and Oxide TFT, and processes are more than 30% complicated. Complex manufacturing processes lead to higher unit prices.
From a manufacturer’s perspective, LTPO application effect must be as large as the increased process unit price. Considering this, it is analyzed that the need and effect of LTPO application are greater (because of the always-on display function) than smartphones. Smartwatches also had a greater effect on lowering power consumption than smartphones. If LTPO is applied, the refresh rate can be lowered, which reduces power consumption, because smartphones require a high refresh rate. The refresh rate is a figure that shows how many scenes are shown per second, and the higher the refresh rate, the smoother the screen transition.
In the case of smartphones, if you play games or watch videos, you can quickly switch to the screen with high refresh rates, allowing you to experience smooth and smooth gaming. Recently released flagship Smartphones are currently supporting 120Hz refresh rate. Considering this trend, LTPO technology, which can reduce screen conversion, is not very suitable for smartphone utilization.
However, in a still picture, LTPS requires a driving of 60Hz to maintain the brightness of the screen due to a high leakage current, but the oxide TFT can be driven at 1Hz because of a low leakage current, so there is no decrease in brightness.
As a result, the LTPO TFT has the effect of reducing the total power in mobile devices by 10% to 15% compared to the LTPS TFT.
To take advantage of LTPO’s technology, new applications and services that consumers want are needed. If it is always turned on and has a function to flow information or a service function to view information by turning on only a certain part of it, OLED and LTPO technologies will be combined and used as an advantage.