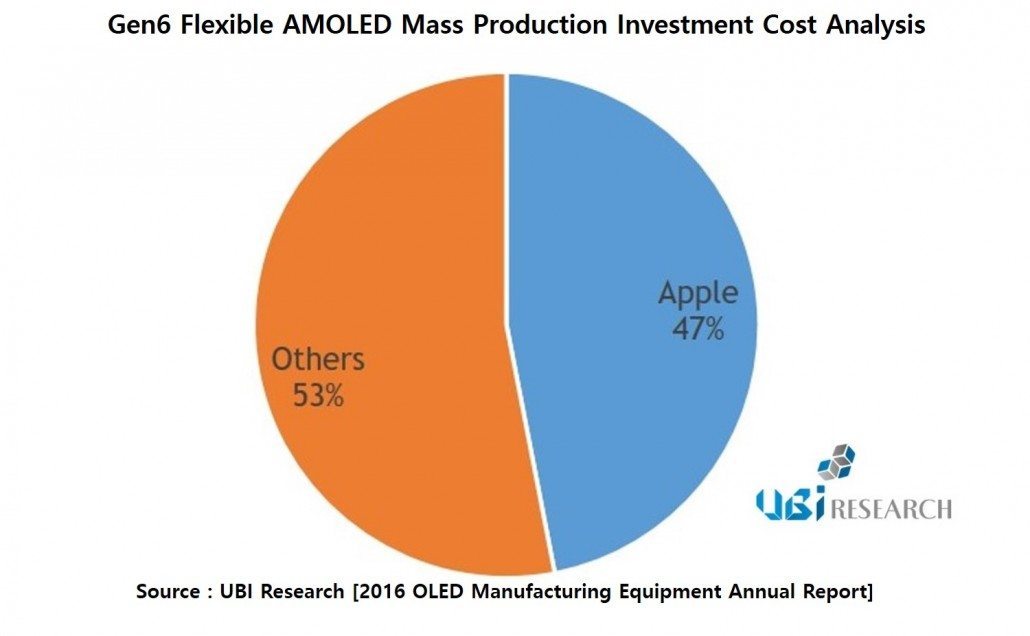
Recent Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics’ TV and smartphone performance results are causing experts to be concerned over degrowth.
The axis that is centering Korean industry is dependent on these 2 companies and Hyundai Motor Company. In the 20th century when technology skills were lacking, Korean government and these 3 companies closely cooperated and coordinated product development and market cultivation. The low value of KRW invigorated the 3 companies’ export business. Strong government support allowed development of products that could compete against Japanese products occupying the international market. The potential that allowed the companies to overtake Japanese firms that were dominating electronics industry and increase the international market share was based on Korean government’s diverse interest and enthusiastic backing.
Japan’s display industry collapsed due to several reasons. Their pride that that latecomers including Korea will not be able to catch up to their technology, the discontinuation of investment by overlooking the need of the 21st century of information for display market, and the disregard of latecomers’ price competitiveness can be attributed to the collapse.
Korean display companies gave up on Gen10 investment in LCD business and began localization in China though establishing Gen8 LCD factory in China. However, Chinse display companies, with the backing of their government in large scale, continue to invest despite the deficit.
If BOE’s Gen10.5 LCD factory is complete, China will lead the global industry in terms of yield, and overtake Korea through China’s domestic market and price competitiveness. Now there are only 2 years left. It is only a question of time before Korea’s LCD industry falls apart.
The only thing that is left for Korean display industry is OLED. As Korean display industry plays an important role in Korean economy, the decline of display industry will have direct impact on employment, export, and domestic market.
However, Korean government is currently ignoring display industry. LCD and OLED have been excluded from WTO’s tariff elimination. China, which is rapidly becoming a new contender in display industry, has agreed with the U.S. to exclude LCD and OLED advocating protection of Chinese market and industry, and other countries followed. China is adding 5% tax for 32inch products or larger; Samsung Display and LG Display are operating LCD factories in China in order to be exempt. The labor force is moving away from Korea to China. Korea’s Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy is overlooking the importance of Korea’s display industry.
To make matters worse, Korean government has no tax regarding manufacturing equipment. When display companies import expensive manufacturing equipment, no tax is added. Recently, due to a low exchange rate of the yen, Japanese companies’ price competitiveness is 1.5 times higher than several years ago. At a time when Korean manufacturing equipment companies are losing heavily in the competition against Japanese, Korean market is actually giving up the market to Japanese companies.
For example, if Samsung Display and LG Display have saved 10,000,000 USD on the purchase of manufacturing equipment, the result is Korean companies’ loss of 100,000,000 USD. Although 10,000,000 USD is a large amount of money to Samsung Display and LG Display, the consequential loss of 100,000,000 USD for Korean manufacturing equipment market is even more immense.
The Korean display ecosystem that has been carefully established is being destroyed by its own government.
Although Korean government is paying lip service to build strong small and medium-sized businesses, in actuality, it is giving small amount of money to large companies and continuing to ignore smaller Korean manufacturing equipment companies. For the future of the smaller Korean manufacturing equipment companies struggling against the weak yen, a system of where they can at the very least survive in domestic market is needed.
Job creation for the young engineers requires more consideration for small and medium-sized businesses rather than large companies that can thrive without any help.